RocketMQ源码通信机制设计
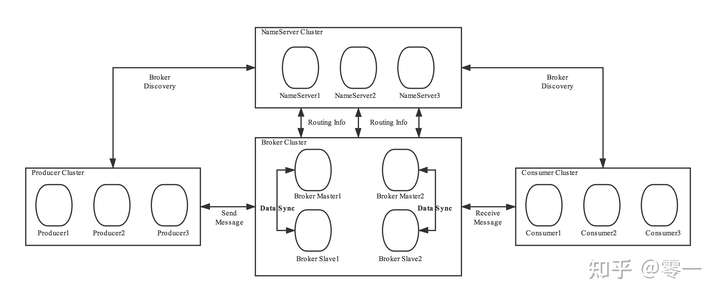
首先我们来看看RocketMQ的基本架构图,RocketMQ主要有NameServer、Producer、Broker、Comumer四个角色,他们之间进行消息的传输主要流程是这样的:
- Broker启动后,将自己的元数据(broker名字、地址等)注册到NameServer,随后定时向NameServer上报Topic路由信息。
- Producer发送消息时,先从本地缓存中获取路由信息,如果没有则会从NameServer中获取路由信息并且更新本地缓存,Producer在启动的时候会启动一个定时任务,每隔30秒从NameServer拉取路由信息。当Producer获取到路由信息时发送消息到Broker,Broker接收Producer发送消息并且落盘保存。
- Comumer接收消息时,同样先从本地缓存中获取路由信息,如果没有则会从NameServer中获取路由信息并且更新本地缓存,Comumer在启动的时候会启动一个定时任务,每隔30秒从NameServer拉取路由信息。Comumer从Broker中拉取消息并且进行消费。
从上面分析得知,Producer会与NameServer、Broker进行通信、Comumer会与NameServer、Broker进行通信,Broker会与NameServer、Broker进行通信。设计一个高效的通信机制是至关重要的,假设由我们来设计这个通信机制,需要考虑哪些问题:
- 通信方式的选择
- 通信协议的设计
- 消息的编解码
RocketMQ自定义了通信协议并在Netty的基础上拓展了通信模块。
假设现在RocketMQ还没有设计通信机制,接下来进行设计。
首先通信的两端分为客户端和服务端,客户端和服务端都有启动、关闭的方法,为了在处理请求之前和返回响应之后做一些事情,采用钩子机制来拓展,所以还需要一个注册钩子的方法,定义的客户端和服务端的公共接口:
package org.apache.rocketmq.remoting;
public interface RemotingService {
//启动
void start();
//关闭
void shutdown();
//注册钩子
void registerRPCHook(RPCHook rpcHook);
}
钩子接口如下:
package org.apache.rocketmq.remoting;
//省略import
public interface RPCHook {
//在处理请求之前调用
void doBeforeRequest(final String remoteAddr, final RemotingCommand request);
//在返回响应之后调用
void doAfterResponse(final String remoteAddr, final RemotingCommand request,
final RemotingCommand response);
}
钩子接口RPCHook有两个方法,分别是doBeforeRequest和doAfterResponse,doBeforeRequest方法在请求之前调用,doAfterResponse在响应之后调用,参数remoteAddr是请求地址,request是请求参数,response是响应参数,类型是RemotingCommand,这个会在下面进行讲述。RPCHook的作用是更好的拓展性,允许用户在请求之前和响应之后做一些事情。
RemotingService接口是客户端和服务端共同的接口,但是客户端和服务端不仅仅有公共的接口和方法,另外还有各自不同的方法,因此,RemotingService接口会有两个客户端子接口RemotingClient和服务端子接口RemotingServer,这两个接口包含着客户端和服务端各自不同的方法。另外客户端和服务端都有一些共同的处理逻辑,为此提供一个抽象类NettyRemotingAbstract进行封装。最后,还需要为接口做具体的实现,采用Netty进行通信,NettyRemotingClient是客户端接口的实现,NettyRemotingServer是服务端接口的实现。接口之间的关系如下:
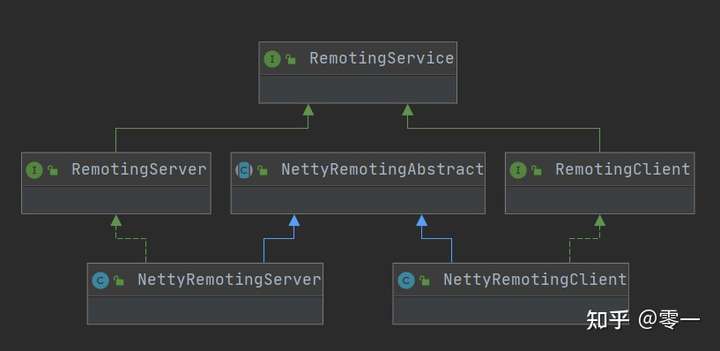
RemotingClient接口
package org.apache.rocketmq.remoting;
//省略import
public interface RemotingClient extends RemotingService {
//更新nameServer的所有地址
void updateNameServerAddressList(final List<String> addrs);
//获取所有的nameServer地址
List<String> getNameServerAddressList();
//同步发送
RemotingCommand invokeSync(final String addr, final RemotingCommand request,
final long timeoutMillis) throws InterruptedException, RemotingConnectException,
RemotingSendRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException;
//异步发送
void invokeAsync(final String addr, final RemotingCommand request, final long timeoutMillis,
final InvokeCallback invokeCallback) throws InterruptedException, RemotingConnectException,
RemotingTooMuchRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException, RemotingSendRequestException;
//单向发送
void invokeOneway(final String addr, final RemotingCommand request, final long timeoutMillis)
throws InterruptedException, RemotingConnectException, RemotingTooMuchRequestException,
RemotingTimeoutException, RemotingSendRequestException;
//注册处理器
void registerProcessor(final int requestCode, final NettyRequestProcessor processor,
final ExecutorService executor);
//设置回调线程执行器
void setCallbackExecutor(final ExecutorService callbackExecutor);
//获取回调执行器
ExecutorService getCallbackExecutor();
//通道是否可写
boolean isChannelWritable(final String addr);
}
RemotingClient接口的方法的作用如上面代码注释所示,设置和获取nameserver地址的方法;不同的发送信息的方法:同步发送、异步发送以及单向发送;注册处理请求的处理器方法以及设置和获取回调线程执行器方法。
RemotingServer接口
package org.apache.rocketmq.remoting;
//省略import
public interface RemotingServer extends RemotingService {
//注册请求处理器
void registerProcessor(final int requestCode, final NettyRequestProcessor processor,
final ExecutorService executor);
//注册默认的请求处理器
void registerDefaultProcessor(final NettyRequestProcessor processor, final ExecutorService executor);
//本地监听端口号
int localListenPort();
//获取处理器与线程执行器的成对关联
Pair<NettyRequestProcessor, ExecutorService> getProcessorPair(final int requestCode);
//同步发送
RemotingCommand invokeSync(final Channel channel, final RemotingCommand request,
final long timeoutMillis) throws InterruptedException, RemotingSendRequestException,
RemotingTimeoutException;
//异步发送
void invokeAsync(final Channel channel, final RemotingCommand request, final long timeoutMillis,
final InvokeCallback invokeCallback) throws InterruptedException,
RemotingTooMuchRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException, RemotingSendRequestException;
//单向发送
void invokeOneway(final Channel channel, final RemotingCommand request, final long timeoutMillis)
throws InterruptedException, RemotingTooMuchRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException,
RemotingSendRequestException;
}
RemotingServer接口与RemotingClient接口类型,也具有注册请求处理器和发送信息的三种方式,另外还具有获取监听端口号和获取处理器与线程执行器的成对关联方法。RemotingServer接口与RemotingClient接口发送信息的方法也是具有同步发送、异步发送、单向发送三种方式,唯一不同的是,RemotingClient接口发送方法的一个参数是连接地址,RemotingServer接口发送方法的一个参数是通道。
NettyRemotingAbstract类
NettyRemotingAbstract类是客户端具体实现类NettyRemotingClient和服务端具体实现类NettyRemotingServer的抽象类,NettyRemotingAbstract类实现NettyRemotingClient和NettyRemotingServer的一些公共方法,不同抽象方法交给NettyRemotingClient和NettyRemotingServer去具体实现。
重要属性
package org.apache.rocketmq.remoting.netty;
public abstract class NettyRemotingAbstract {
//限制最大的单向发送请求次数
protected final Semaphore semaphoreOneway;
//限制最大发送异步请求次数
protected final Semaphore semaphoreAsync;
//保存请求id与对应响应之间的关系
protected final ConcurrentMap<Integer /* opaque */, ResponseFuture> responseTable =
new ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, ResponseFuture>(256);
//保存请求码与处理器、处理器执行线程的关系
protected final HashMap<Integer/* request code */, Pair<NettyRequestProcessor, ExecutorService>> processorTable =
new HashMap<Integer, Pair<NettyRequestProcessor, ExecutorService>>(64);
//netty事件线程执行器
protected final NettyEventExecutor nettyEventExecutor = new NettyEventExecutor();
//默认的请求处理器和处理器执行线程
protected Pair<NettyRequestProcessor, ExecutorService> defaultRequestProcessor;
//自定义的RPC钩子
protected List<RPCHook> rpcHooks = new ArrayList<RPCHook>();
//省略代码
}
NettyRemotingAbstract类的一些重要属性如上述代码所示,为了限制单向发送和异步发送的频率,保护服务器,采用Semaphore信号量进行限制,只有获取到信号量,才可以进行请求的处理。
responseTable属性保存着请求id和响应之间的关系,通过请求id就可以获取到对应的响应了。
processorTable属性保存着请求码与请求处理器、请求处理器执行线程的关系,不同的请求通过请求码交给不同的请求处理器进行处理。
nettyEventExecutor属性是netty事件线程执行器,当接收到不同netty事件,如闲置事件、关闭事件、连接事件、异常事件,会放进队列中,线程会不断从队列中取出事件,然后进行不同事件的处理。
defaultRequestProcessor是默认的请求处理器,当通过请求码没有找到对应的处理器时,就交给默认处理器处理。
rpcHooks是保存自定义的RPC钩子,在处理请求和响应时,会调用钩子的方法。
具体看看NettyEventExecutor的实现:
class NettyEventExecutor extends ServiceThread {
//保存netty事件队列
private final LinkedBlockingQueue<NettyEvent> eventQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<NettyEvent>();
private final int maxSize = 10000;
//将事件添加到队列中
public void putNettyEvent(final NettyEvent event) {
if (this.eventQueue.size() <= maxSize) {
this.eventQueue.add(event);
} else {
log.warn("event queue size[{}] enough, so drop this event {}", this.eventQueue.size(), event.toString());
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started");
//通道事件监听器
final ChannelEventListener listener = NettyRemotingAbstract.this.getChannelEventListener();
//线程一直运行
while (!this.isStopped()) {
try {
//从队列中不断拿出事件,根据事件类型调用事件监听器的不同处理方法
NettyEvent event = this.eventQueue.poll(3000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (event != null && listener != null) {
switch (event.getType()) {
case IDLE:
listener.onChannelIdle(event.getRemoteAddr(), event.getChannel());
break;
case CLOSE:
listener.onChannelClose(event.getRemoteAddr(), event.getChannel());
break;
case CONNECT:
listener.onChannelConnect(event.getRemoteAddr(), event.getChannel());
break;
case EXCEPTION:
listener.onChannelException(event.getRemoteAddr(), event.getChannel());
break;
default:
break;
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn(this.getServiceName() + " service has exception. ", e);
}
}
log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end");
}
@Override
public String getServiceName() {
return NettyEventExecutor.class.getSimpleName();
}
}
NettyEventExecutor类是NettyRemotingAbstract类的一个内部类,实现上也是一个线程。eventQueue是一个保存事件的阻塞队列,最大只能保存10000个事件,当超过最大的容量时,将事件丢弃。NettyEventExecutor启动时,不断从队列中取出事件,根据事件类型将事件交给通道监听器的不同方法进行处理。
在NettyRemotingAbstract类中,将添加事件委托给NettyEventExecutor类putNettyEvent方法进行添加到队列中。
重要方法
处理接收到消息的方法:
public void processMessageReceived(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RemotingCommand msg) throws Exception {
final RemotingCommand cmd = msg;
if (cmd != null) {
//类型
switch (cmd.getType()) {
//请求
case REQUEST_COMMAND:
processRequestCommand(ctx, cmd);
break;
//响应
case RESPONSE_COMMAND:
processResponseCommand(ctx, cmd);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
processMessageReceived是处理接收到消息的方法,根据类型判断,将请求类型交给processRequestCommand方法处理,将响应类型交给processResponseCommand方法处理。
处理请求
public void processRequestCommand(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx, final RemotingCommand cmd) {
//根据请求码获取处理器、处理器执行线程
final Pair<NettyRequestProcessor, ExecutorService> matched = this.processorTable.get(cmd.getCode());
//通过请求码没有找到则使用morning的处理器
final Pair<NettyRequestProcessor, ExecutorService> pair = null == matched ? this.defaultRequestProcessor : matched;
//请求id
final int opaque = cmd.getOpaque();
if (pair != null) {
//处理请求以及响应的逻辑
Runnable run = new Runnable() {
//省略run方法代码
};
//如果处理器拒绝请求,则直接返回系统忙碌的响应
if (pair.getObject1().rejectRequest()) {
final RemotingCommand response = RemotingCommand.createResponseCommand(RemotingSysResponseCode.SYSTEM_BUSY,
"[REJECTREQUEST]system busy, start flow control for a while");
response.setOpaque(opaque);
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
return;
}
//将上面的run包装成请求任务,并且提交给线程进行执行
try {
final RequestTask requestTask = new RequestTask(run, ctx.channel(), cmd);
pair.getObject2().submit(requestTask);
} catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
//发生拒绝执行异常
//打印系统忙碌的日志
if ((System.currentTimeMillis() % 10000) == 0) {
log.warn(RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(ctx.channel())
+ ", too many requests and system thread pool busy, RejectedExecutionException "
+ pair.getObject2().toString()
+ " request code: " + cmd.getCode());
}
//如果不是单向的RPC请求,则返回系统忙碌的响应
if (!cmd.isOnewayRPC()) {
final RemotingCommand response = RemotingCommand.createResponseCommand(RemotingSysResponseCode.SYSTEM_BUSY,
"[OVERLOAD]system busy, start flow control for a while");
response.setOpaque(opaque);
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
}
}
} else {
//如果没有处理器,则返回请求类型不支持的响应
String error = " request type " + cmd.getCode() + " not supported";
final RemotingCommand response =
RemotingCommand.createResponseCommand(RemotingSysResponseCode.REQUEST_CODE_NOT_SUPPORTED, error);
response.setOpaque(opaque);
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
log.error(RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(ctx.channel()) + error);
}
}
processRequestCommand方法首先根据请求码获取处理器、处理器执行线程,如果获取不到请求处理器和处理器执行线程,则采用默认的请求处理器和线程执行器。当通过上述操作,处理器还是为空的话,则返回请求类型不支持的响应,如果处理器不为空,将处理请求和响应的逻辑封装在Runnable类的run方法中,这里先省略run方法的具体逻辑,等到下面再进行讲述。如果处理器的拒绝请求,则则直接返回系统忙碌的响应,然后将请求逻辑包装成请求任务,并且提交给线程进行执行。线程在执行过程中发生拒绝执行异常,则进行打印系统繁忙的日志,如果不是单向的RPC发送请求,则返回系统忙碌的响应。
接下来我们看看省略掉run方法:
public void run() {
try {
//执行RPC钩子,请求之前
doBeforeRpcHooks(RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(ctx.channel()), cmd);
//响应回调
final RemotingResponseCallback callback = new RemotingResponseCallback() {
@Override
public void callback(RemotingCommand response) {
//执行RPC钩子,响应之后
doAfterRpcHooks(RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(ctx.channel()), cmd, response); //如果不是单向请求
if (!cmd.isOnewayRPC()) {
//响应不为空,将响应返回
if (response != null) {
response.setOpaque(opaque);
response.markResponseType();
try {
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("process request over, but response failed", e);
log.error(cmd.toString());
log.error(response.toString());
}
} else {
}
}
}
};
//如果是异步处理器
if (pair.getObject1() instanceof AsyncNettyRequestProcessor) {
AsyncNettyRequestProcessor processor = (AsyncNettyRequestProcessor)pair.getObject1();
//异步处理请求请求
processor.asyncProcessRequest(ctx, cmd, callback);
} else {
//同步处理请求
NettyRequestProcessor processor = pair.getObject1();
RemotingCommand response = processor.processRequest(ctx, cmd);
doAfterRpcHooks(RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(ctx.channel()), cmd, response); //响应回调
callback.callback(response);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("process request exception", e);
log.error(cmd.toString());
//如果不是单向RPC请求,直接返回系统错误
if (!cmd.isOnewayRPC()) {
final RemotingCommand response = RemotingCommand.createResponseCommand(RemotingSysResponseCode.SYSTEM_ERROR,
RemotingHelper.exceptionSimpleDesc(e));
response.setOpaque(opaque);
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
}
}
}
run方法的逻辑也不难,在请求处理之前,遍历所有钩子并执行钩子的请求之前方法,判断处理器是同步处理器还是异步处理器,如果是异步处理器,那么就通过异步处理器的异步处理方法处理请求,否则通过同步处理器的同步处理方法处理请求,等同步处理器处理完请求时,则调用响应的回调方法,回调方法会遍历所有钩子并执行钩子的响应之后方法。在处理器处理请求时,如果发生异常,并且请求不是单向的,则直接返回系统错误的响应。
处理响应
public void processResponseCommand(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RemotingCommand cmd) {
//获取请求id
final int opaque = cmd.getOpaque();
//响应future
final ResponseFuture responseFuture = responseTable.get(opaque);
if (responseFuture != null) {
responseFuture.setResponseCommand(cmd);
//根据请求id删除保存的响应
responseTable.remove(opaque);
//执行回调不为空,执行回调方法
if (responseFuture.getInvokeCallback() != null) {
executeInvokeCallback(responseFuture);
} else {
//设置响应
responseFuture.putResponse(cmd);
//释放响应future
responseFuture.release();
}
} else {
log.warn("receive response, but not matched any request, " + RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(ctx.channel()));
log.warn(cmd.toString());
}
}
processResponseCommand方法通过请求id从缓存中获取到对应的响应future,当响应future不为空时,则删除保存在缓存中的响应future,并且判断响应回调方法是否为空,如果不是则执行回调方法,否则释放响应future。
扫描请求的响应
在讲述重要属性中,我们知道请求与响应的对应关系是通过responseTable保存的,通过请求id就能获取到对应的响应,当接收到异步请求时,就将请求id和响应保存在responseTable中,然后进行异步处理请求,如果请求已经超时了,那么就直接处理响应了,scanResponseTable方法就是干这件事情的。
public void scanResponseTable() {
//保存已经过期的响应
final List<ResponseFuture> rfList = new LinkedList<ResponseFuture>();
Iterator<Entry<Integer, ResponseFuture>> it = this.responseTable.entrySet().iterator();
//遍历所有的响应,过滤出已经过期的响应
while (it.hasNext()) {
Entry<Integer, ResponseFuture> next = it.next();
ResponseFuture rep = next.getValue();
//已经过期,则释放响应,并删除缓存,保存到list
if ((rep.getBeginTimestamp() + rep.getTimeoutMillis() + 1000) <= System.currentTimeMillis()) {
rep.release();
it.remove();
rfList.add(rep);
log.warn("remove timeout request, " + rep);
}
}
//遍历已经过期的响应,然后执行响应回调方法
for (ResponseFuture rf : rfList) {
try {
executeInvokeCallback(rf);
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.warn("scanResponseTable, operationComplete Exception", e);
}
}
}
scanResponseTable方法遍历保存在responseTable的所有响应,如果过期则从responseTable删除,并将过滤的响应保存到list中。后续遍历已经过期的响应列表,执行响应回调方法。在客户端和服务端启动的时候,都会启动一个定时任务调用scanResponseTable方法扫描已经过期的响应。
发送信息
客户端和服务端发送信息有三种方式:单向发送、同步发送、异步发送。
单向发送:顾名思义就是只管发送信息,不需要返回响应。
同步发送:发送信息以后,一直阻塞到响应返回,超时也会返回响应。
异步发送:发送信息以后,不等待响应的返回,异步处理请求。
单向发送
public void invokeOnewayImpl(final Channel channel, final RemotingCommand request, final long timeoutMillis)
throws InterruptedException, RemotingTooMuchRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException, RemotingSendRequestException {
//设置单向发送的标志
request.markOnewayRPC();
//尝试获取信号量,进行单向发送请求限流
boolean acquired = this.semaphoreOneway.tryAcquire(timeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
//如果获取到信号量,则进行发送信息
if (acquired) {
final SemaphoreReleaseOnlyOnce once = new SemaphoreReleaseOnlyOnce(this.semaphoreOneway);
try {
//发送消息,并且监听响应释放信号量
channel.writeAndFlush(request).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture f) throws Exception {
//释放信号量
once.release();
//如果不成功,则打印日志
if (!f.isSuccess()) {
log.warn("send a request command to channel <" + channel.remoteAddress() + "> failed.");
}
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
//释放信号量
once.release();
log.warn("write send a request command to channel <" + channel.remoteAddress() + "> failed.");
//抛出异常
throw new RemotingSendRequestException(RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(channel), e);
}
} else {
//没有获取到信号量,如果超时时间小于等于0,抛出异常请求太快异常
if (timeoutMillis <= 0) {
throw new RemotingTooMuchRequestException("invokeOnewayImpl invoke too fast");
} else {
//获取信号超时,抛出异常
String info = String.format(
"invokeOnewayImpl tryAcquire semaphore timeout, %dms, waiting thread nums: %d semaphoreAsyncValue: %d",
timeoutMillis,
this.semaphoreOneway.getQueueLength(),
this.semaphoreOneway.availablePermits()
);
log.warn(info);
throw new RemotingTimeoutException(info);
}
}
}
invokeOnewayImpl通过Semaphore信号量进行限流,只有获取到信号量,才进行请求。如果获取信号量失败,则抛出异常给请求端进行处理。如果获取信号量成功,通过netty将请求发送出去,并且监听响应,但是并没有将响应返回,当请求完成后释放信号量。如果发送出现异常,也是抛出异常。
同步发送
public RemotingCommand invokeSyncImpl(final Channel channel, final RemotingCommand request,
final long timeoutMillis)
throws InterruptedException, RemotingSendRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException {
//获取请求id
final int opaque = request.getOpaque();
try {
//创建响应future
final ResponseFuture responseFuture = new ResponseFuture(channel, opaque, timeoutMillis, null, null);
//将响应future添加到responseTable
this.responseTable.put(opaque, responseFuture);
final SocketAddress addr = channel.remoteAddress();
//发送信息
channel.writeAndFlush(request).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture f) throws Exception {
//如果成功发送,设置发送请求成功标志
if (f.isSuccess()) {
responseFuture.setSendRequestOK(true);
return;
} else {
//请求失败
responseFuture.setSendRequestOK(false);
}
//从responseTable删除响应future
responseTable.remove(opaque);
//设置原因
responseFuture.setCause(f.cause());
responseFuture.putResponse(null);
log.warn("send a request command to channel <" + addr + "> failed.");
}
});
//等待响应返回
RemotingCommand responseCommand = responseFuture.waitResponse(timeoutMillis);
//响应为空
if (null == responseCommand) {
if (responseFuture.isSendRequestOK()) {
//超时异常
throw new RemotingTimeoutException(RemotingHelper.parseSocketAddressAddr(addr), timeoutMillis,
responseFuture.getCause());
} else {
//请求异常
throw new RemotingSendRequestException(RemotingHelper.parseSocketAddressAddr(addr), responseFuture.getCause());
}
}
//返回响应
return responseCommand;
} finally {
//删除响应future
this.responseTable.remove(opaque);
}
}
同步发送首先获取请求id,并创建响应future,将请求id和响应future添加到responseTable,然后发送请求并等待响应返回,同样,同步发送也会监听发送请求是否已经完成,当请求完成时,设置响应future的相关属性并且从responseTable删除响应future。当响应返回时,如果响应为空,根据发送是否成功标志,抛出超时异常或者请求异常。
异步发送
public void invokeAsyncImpl(final Channel channel, final RemotingCommand request, final long timeoutMillis,
final InvokeCallback invokeCallback)
throws InterruptedException, RemotingTooMuchRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException, RemotingSendRequestException {
//请求开始时间
long beginStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//请求id
final int opaque = request.getOpaque();
//获取信号量
boolean acquired = this.semaphoreAsync.tryAcquire(timeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (acquired) {
final SemaphoreReleaseOnlyOnce once = new SemaphoreReleaseOnlyOnce(this.semaphoreAsync);
long costTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginStartTime;
//判断是否已经超时了,超时抛出超时异常
if (timeoutMillis < costTime) {
once.release();
throw new RemotingTimeoutException("invokeAsyncImpl call timeout");
}
//创建响应future
final ResponseFuture responseFuture = new ResponseFuture(channel, opaque, timeoutMillis - costTime, invokeCallback, once);
//将请求id和响应future添加到responseTable
this.responseTable.put(opaque, responseFuture);
try {
//发送信息,并且监听请求已经完成
channel.writeAndFlush(request).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture f) throws Exception {
//如果成功,设置发送请求标志
if (f.isSuccess()) {
responseFuture.setSendRequestOK(true);
return;
}
//如果失败,则从responseTable删除响应future,并且调用响应回调方法
requestFail(opaque);
log.warn("send a request command to channel <{}> failed.", RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(channel));
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
//发生异常,释放responseFuture,抛出发送请求异常
responseFuture.release();
log.warn("send a request command to channel <" + RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(channel) + "> Exception", e);
throw new RemotingSendRequestException(RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(channel), e);
}
} else {
//抛出异常,超时请求、请求太快异常
if (timeoutMillis <= 0) {
throw new RemotingTooMuchRequestException("invokeAsyncImpl invoke too fast");
} else {
String info =
String.format("invokeAsyncImpl tryAcquire semaphore timeout, %dms, waiting thread nums: %d semaphoreAsyncValue: %d",
timeoutMillis,
this.semaphoreAsync.getQueueLength(),
this.semaphoreAsync.availablePermits()
);
log.warn(info);
throw new RemotingTimeoutException(info);
}
}
}
invokeAsyncImpl异步发送方法与同步发送方法类似,都是将请求id和响应future保存到responseTable中,然后获取到信号才进行发送信息,对请求进行监听,唯一不同的就是,不用阻塞等到响应,也不用将响应返回,而是在请求完成时,将调用响应回调方法,对返回的响应交给回调方法进行处理。
NettyRemotingClient类
NettyRemotingClient类的定义如下:
public class NettyRemotingClient extends NettyRemotingAbstract implements RemotingClient {
//代码省略
}
NettyRemotingClient类继承了NettyRemotingAbstract方法,并且实现了RemotingClient接口。接下来只分析NettyRemotingClient类的start方法,其他方法比较简单,或者是调用了NettyRemotingAbstract的方法,在NettyRemotingAbstract方法的基础上添加了一些简单的逻辑,所以这里就进行分析,直接看源码也是比较简单的。
public void start() {
//创建默认的事件执行组
this.defaultEventExecutorGroup = new DefaultEventExecutorGroup(
nettyClientConfig.getClientWorkerThreads(),
new ThreadFactory() {
private AtomicInteger threadIndex = new AtomicInteger(0);
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, "NettyClientWorkerThread_" + this.threadIndex.incrementAndGet());
}
});
//客户端启动器
Bootstrap handler = this.bootstrap.group(this.eventLoopGroupWorker).channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true) // tcp无延迟
.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, false) //不保持长链接
//连接超时时间
.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, nettyClientConfig.getConnectTimeoutMillis())
//发送缓存大小
.option(ChannelOption.SO_SNDBUF, nettyClientConfig.getClientSocketSndBufSize())
//接收缓冲大小
.option(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, nettyClientConfig.getClientSocketRcvBufSize())
//处理器
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
if (nettyClientConfig.isUseTLS()) {
if (null != sslContext) {
pipeline.addFirst(defaultEventExecutorGroup, "sslHandler", sslContext.newHandler(ch.alloc()));
log.info("Prepend SSL handler");
} else {
log.warn("Connections are insecure as SSLContext is null!");
}
}
pipeline.addLast(
defaultEventExecutorGroup,
new NettyEncoder(), //编码
new NettyDecoder(), //解码
//空闲处理器
new IdleStateHandler(0, 0, nettyClientConfig.getClientChannelMaxIdleTimeSeconds()),
//连接管理处理器
new NettyConnectManageHandler(),
//netty客户端处理器
new NettyClientHandler());
}
});
//定时任务扫描响应
this.timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
NettyRemotingClient.this.scanResponseTable();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("scanResponseTable exception", e);
}
}
}, 1000 * 3, 1000);
//启动通道事件处理监听器
if (this.channelEventListener != null) {
this.nettyEventExecutor.start();
}
}
start方法主要做了几件事:
- 为客户端启动器,设置各种属性参数、处理器,并且启动了netty客户端。处理器包括编码处理器、解码处理器、netty客户端管理器实际就是调用NettyRemotingAbstract的processMessageReceived方法处理接收到的信息,processMessageReceived 方法的分析已经在上面讲述过了。编码处理器、解码处理器内容将在下面讲述通信协议的设计以及通信编解码进行讲述。
- 定时任务扫描响应,调用NettyRemotingAbstract的scanResponseTable方法扫描过期的响应。这部分内容已经再上面分析过了。
- 启动通道事件监听器,就是调用NettyRemotingAbstract的内部类NettyEventExecutor的start方法,启动线程不断从队列中取出事件,根据事件类型进行调用监听器的不同处理方法,这部分内容也在NettyRemotingAbstract分析中讲述过了。
NettyRemotingServer类
NettyRemotingServer类的定义如下:
public class NettyRemotingServer extends NettyRemotingAbstract implements RemotingServer {
//代码省略
}
NettyRemotingServer类继承了NettyRemotingAbstract方法,并且实现了RemotingServer接口。NettyRemotingServer类的大部分方法都是在NettyRemotingAbstract类的基础上增加了一些简单的逻辑。同样,NettyRemotingServer类也只分析start方法。
public void start() {
//创建默认的事件执行组
this.defaultEventExecutorGroup = new DefaultEventExecutorGroup(
nettyServerConfig.getServerWorkerThreads(),
new ThreadFactory() {
private AtomicInteger threadIndex = new AtomicInteger(0);
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, "NettyServerCodecThread_" + this.threadIndex.incrementAndGet());
}
});
//初始化共享的处理器
prepareSharableHandlers();
//服务启动器
ServerBootstrap childHandler =
this.serverBootstrap.group(this.eventLoopGroupBoss, this.eventLoopGroupSelector)
.channel(useEpoll() ? EpollServerSocketChannel.class : NioServerSocketChannel.class)
//日志大小
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024)
//
.option(ChannelOption.SO_REUSEADDR, true)
//不保持长链接
.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, false)
//tcp不延迟
.childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
//发送缓冲大小
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_SNDBUF, nettyServerConfig.getServerSocketSndBufSize())
//接收缓冲大小
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, nettyServerConfig.getServerSocketRcvBufSize())
.localAddress(new InetSocketAddress(this.nettyServerConfig.getListenPort()))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline()
.addLast(defaultEventExecutorGroup, HANDSHAKE_HANDLER_NAME, handshakeHandler)
.addLast(defaultEventExecutorGroup,
encoder,//编码
new NettyDecoder(),//解码
new IdleStateHandler(0, 0, nettyServerConfig.getServerChannelMaxIdleTimeSeconds()),
connectionManageHandler, //连接处理器
serverHandler // 服务处理器
);
}
});
if (nettyServerConfig.isServerPooledByteBufAllocatorEnable()) {
childHandler.childOption(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT);
}
try {
//启动服务启动器
ChannelFuture sync = this.serverBootstrap.bind().sync();
InetSocketAddress addr = (InetSocketAddress) sync.channel().localAddress();
this.port = addr.getPort();
} catch (InterruptedException e1) {
throw new RuntimeException("this.serverBootstrap.bind().sync() InterruptedException", e1);
}
//启动事件监听器
if (this.channelEventListener != null) {
this.nettyEventExecutor.start();
}
//定时扫描响应
this.timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
NettyRemotingServer.this.scanResponseTable();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("scanResponseTable exception", e);
}
}
}, 1000 * 3, 1000);
}
start方法主要做了几件事:
- 初始化处理器
- 设置服务启动器的属性、处理器,并启动服务启动器。处理器包括编解码处理器、连接管理处理器、服务处理器。
- 启动事件监听器。
- 定时扫描响应。
协议设计与编解码
在客户端和服务端之间传输消息,需要对发送的消息进行一个协议约定,客户端和服务端才能对消息进行编解码。在RocketMQ中,RemotingCommand是所有传输数据的封装,也包括对数据的编解码。
public class RemotingCommand {
private int code;
private LanguageCode language = LanguageCode.JAVA;
private int version = 0;
private int opaque = requestId.getAndIncrement();
private int flag = 0;
private String remark;
private HashMap<String, String> extFields;
private transient CommandCustomHeader customHeader;
private SerializeType serializeTypeCurrentRPC = serializeTypeConfigInThisServer;
private transient byte[] body;
//省略代码
}
下面是上面属性的解释:
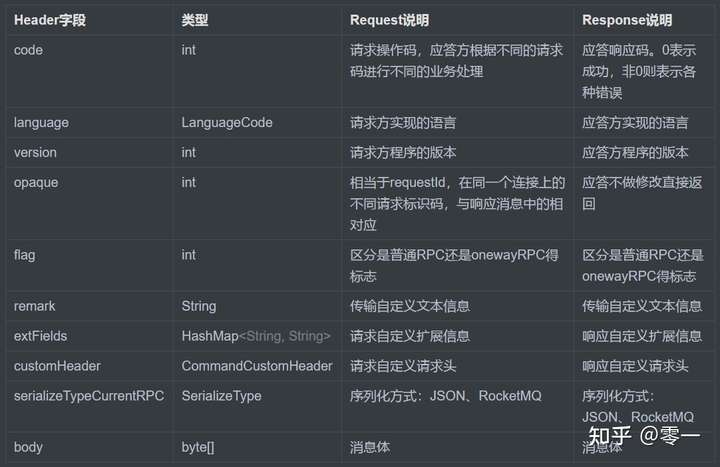
客户端和服务端内容可以分为四部分内容:
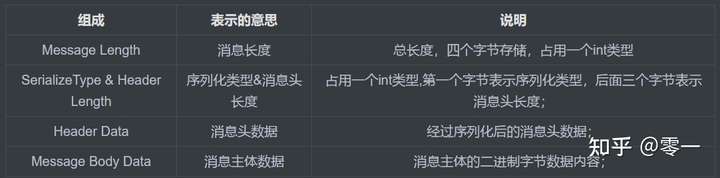
编码
public ByteBuffer encode() {
//请求头长度
// 1> header length size
int length = 4;
//请求头数据长度
// 2> header data length
byte[] headerData = this.headerEncode();
length += headerData.length;
//消息体数据长度
// 3> body data length
if (this.body != null) {
length += body.length;
}
//申请的内存大小:4 + length,4 表示消息存储的大小
ByteBuffer result = ByteBuffer.allocate(4 + length);
// length 写入长度
result.putInt(length);
// header length 序列化、请求头长度
result.put(markProtocolType(headerData.length, serializeTypeCurrentRPC));
// header data 请求头数据
result.put(headerData);
// body data; // 请求体数据
if (this.body != null) {
result.put(this.body);
}
result.flip();
return result;
}
编码的过程就是根据通讯协议,计算需要的内存大小,序列化数据,按照长度、请求头长度、请求头数据、请求体数据写入到ByteBuffer中。序列化的方式有JSON和ROCKETMQ两种。序列化需要将请求头数据和消息体数据转出二进制字节数组。
解码
public static RemotingCommand decode(final ByteBuffer byteBuffer) {
//总长度
int length = byteBuffer.limit();
//请求头和序列化长度
int oriHeaderLen = byteBuffer.getInt();
//请求头长度
int headerLength = getHeaderLength(oriHeaderLen);
//请求头数据
byte[] headerData = new byte[headerLength];
//获取请求头数据
byteBuffer.get(headerData);
//将请求头数据解析出来转换成RemotingCommand
RemotingCommand cmd = headerDecode(headerData, getProtocolType(oriHeaderLen));
//请求体长度:总长度-消息大小(4个字节)-请求头长度
int bodyLength = length - 4 - headerLength;
byte[] bodyData = null;
//获取请求体数据
if (bodyLength > 0) {
bodyData = new byte[bodyLength];
byteBuffer.get(bodyData);
}
cmd.body = bodyData;
return cmd;
}
解码过程是编码的反过程,从ByteBuffer中读取出总长度、序列化类型、请求头长度、请求头数据、请求体长度、请求数据。